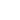
Tungsten prices have risen by over 200% year-to-date in late 2025, reaching a nearly two-decade high due to a severe supply crunch and surging demand.
Tungsten (primarily tungsten carbide) is critical for drill bits,milling tools, wear-resistant parts/tools, and weighting materials in drilling. Its steep price increase presents multi-faceted challenges:
I. Sharp Rise in Direct Costs and Severe Profit Margin Erosion
- Dramatic Increase in Drill Bit Manufacturing Costs
- Tungsten carbide is a core material for tricone drill bits (TCI), PDC drill bit matrices and polycrystalline diamond compact welding layers, accounting for 15-25% of the total raw material cost of drill bits.
- The prices of key raw materials such as tungsten and cobalt have increased by 15-20% compared with 2022, leading to an 8-10% rise in the production cost of tricone drill bits.
- Matrix-type PDC drill bits consume large quantities of tungsten carbide powder, and the price hike directly drives up the cost of matrix manufacturing.
- Increase in Total Drilling Operation Costs
- Drill bits are one of the most consumed components in the drilling process, and the price increase is directly passed on to drilling service fees.
- In high-hardness formation drilling, the service life of tungsten carbide drill bits is more than 50 times longer than that of ordinary steel bits, making it impossible to replace them easily, and thus the cost pressure is unavoidable.
- In addition to drill bits, the prices of tungsten carbide components such as drill pipe valve seats, sandblasting nozzles and wear-resistant pipe liners have also risen simultaneously, further increasing operation costs.
- Dual Squeeze on Corporate Profits
- The growth rate of upstream raw material prices outpaces that of downstream product price hikes, resulting in a lag in cost pass-through.
- Fierce market competition, especially among small and medium-sized drilling enterprises, limits their room for price increases, with some enterprises seeing their gross profit margins fall below 10%.
- International giants such as Sandvik announced a 22% product price increase, which still failed to fully cover the cost growth, leaving small and medium-sized enterprises in a more difficult position.
II. Challenges to Supply Chain Security and Stability
- Strengthened Strategic Resource Control Aggravates Supply Shortage
- Tungsten has been included in the “list of critical strategic metals” by the EU, the United States, Japan and other regions, leading to tightened export controls and supply chain reviews.
- As the world’s largest tungsten resource producer (accounting for over 80% of global reserves), China implemented export controls in February 2025, requiring “one license per order” for 25 rare metals including ammonium paratungstate.
- The rapid growth in demand from high-end manufacturing and new energy sectors (such as photovoltaic tungsten wires and nuclear fusion) has intensified the competition for limited resources with the drilling industry.
- Supply-Demand Imbalance Fuels Price Volatility
- Global tungsten demand is expected to exceed 130,000 tons in 2025, an increase of about 6% year-on-year, while supply growth remains limited.
- The grade of domestic tungsten ore resources has declined, with the average grade of raw ore dropping from 0.42% in 2024 to 0.28%, pushing up mining costs.
- Strict environmental protection policies have restricted tungsten ore mining, further squeezing the supply side.
- Risk of Supply Disruption for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
- Approximately 30% of small and medium-sized European tool enterprises have been forced to suspend order acceptance due to supply shortages or high costs.
- Drilling enterprises may face delivery delays of key components such as drill bits, affecting project progress and contract performance.
III. Growing Pressure on Technology Selection and Innovation
- Challenges in Material Substitution R&D
- Tungsten carbide has significant performance advantages in high-pressure, high-impact and sand-wear environments, making it difficult to find a complete substitute in the short term.
- Developing cost-effective alternative materials or coating technologies requires substantial R&D investment and time for verification.
- Spherical tungsten carbide offers better performance than angular tungsten carbide but costs 3-4 times more, putting technical selection in a dilemma between “cost and performance”.
- Pressure to Optimize Processes and Improve Efficiency
- Enterprises have been forced to intensify process improvement efforts, such as redesigning the steel core structure of PDC drill bits to reduce tungsten carbide powder consumption (the new process can lower costs by 54%).
- Improving raw material utilization rates, leading enterprises have increased their utilization rate from 85% to 92%.
- Recycling and reusing waste drill bits has become an important direction, and the proportion of recycled materials needs to be increased to more than 25% to effectively alleviate cost pressure.
- Risks of Adjusting Technical Routes
- Some enterprises may switch to low-cost alternatives such as steel-tooth drill bits, but their low efficiency and short service life in hard formations will instead increase the overall cost.
- High-end drilling projects (such as deep-sea and high-temperature high-pressure wells) have a high dependence on tungsten carbide performance, leaving little room for technical adjustments and resulting in greater cost pressure.
IV. Market Competition and Restructuring of Industry Landscape
- Increased Industry Concentration
- Large enterprises are better able to withstand the impact of rising prices thanks to their economies of scale, technological advantages and supply chain control capabilities.
- Small and medium-sized enterprises may be eliminated or acquired due to weak cost control capabilities and limited financing channels.
- The global tungsten carbide supply chain is concentrating in leading enterprises, further exacerbating industry differentiation.
- Intensified International Market Competition
- China’s export controls have changed the global tungsten carbide supply pattern, exposing European and American enterprises to dual pressures of supply shortages and price increases.
- Enterprises in emerging market countries may gain more market share due to cost advantages, changing the competitive landscape of the global drilling equipment market.
- Tariff policies and trade barriers have become more complex, increasing the costs and uncertainties of international business.
- Changes in Customer Demand
- Oil companies may reduce exploration and development budgets, delay or cancel new projects, and lower the demand for drilling services.
- Customers are more inclined to choose cost-effective drilling solutions and put forward higher requirements for the service life and efficiency of drill bits.
- Price adjustment clauses in long-term contracts have become a key focus of negotiations, increasing the costs and risks of business communication.
Post time: Jan-13-2026








 5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China
5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China  86-13609153141
86-13609153141 

