Long auger drills and short auger drills are two common drilling tools, mainly used for drilling operations in loose formations such as soil and sand-gravel. Their core difference lies in the length of the auger flights and applicable scenarios.
I.Long Auger Drill (Full Auger Drill)
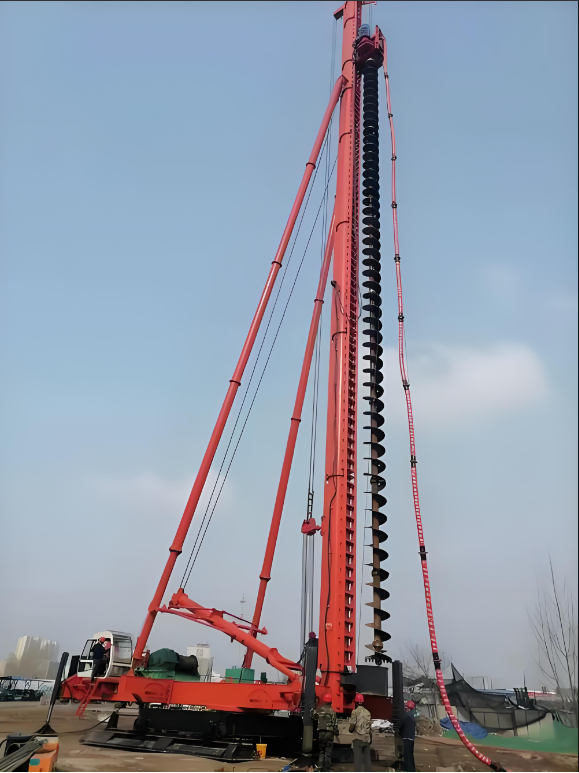 1.Working Principle
1.Working Principle
Rotational Cutting: Driven by the power head, the drill bit rotates to cut soil layers or soft rock, and the broken dregs are captured by the auger flights.
Continuous Slag Discharge: The auger flights cover the drill pipe throughout its length. During rotation, a “screw conveyor effect” is formed, and the dregs are continuously conveyed upward to the hole mouth along the flights, realizing “drilling while discharging”. Slag discharge can be completed without lifting the drill.
Dry Operation Hole Formation: Generally, no mud or casing is required for hole wall protection (but casing can be used in loose formations), and a bare hole is formed directly.
2.Structural Features
The auger flights are long (usually several meters to tens of meters), with an integrated design with the drill pipe.
The flights are continuously distributed and can cover the entire drilling depth.
3.Applicable Scenarios
Formations: Loose soil layers, silty soil, sand layers, etc.; not suitable for hard rock or large-grain pebble layers.
Project Types: Building pile foundations (e.g., CFG piles, cast-in-place piles), shallow geological exploration, etc.
Advantages: Fast drilling speed, high slag discharge efficiency, and good hole formation quality.
4.Limitations
Drilling depth is limited by drill pipe stiffness and torque (generally ≤30m).
Hole collapse is prone to occur when the groundwater level is high, requiring the use of casing.
II.Short Auger Drill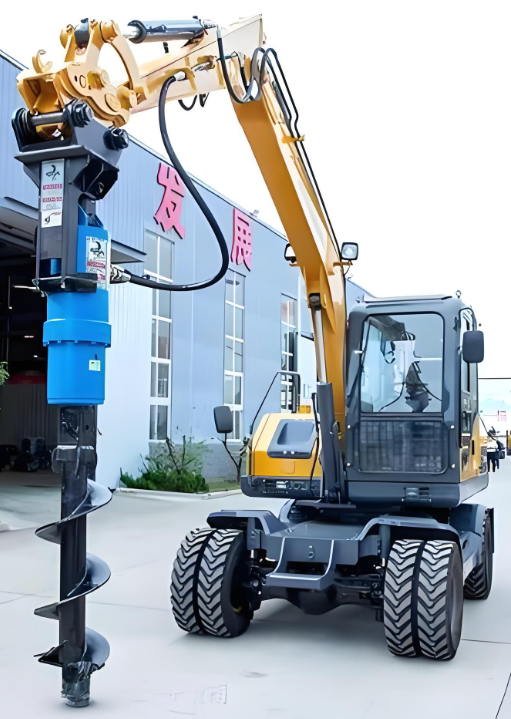
1.Working Principle
Rotational Cutting: The drill bit rotates to break the soil layer, and the dregs are temporarily stored in the short auger flights near the drill bit.
Intermittent Slag Discharge: Due to the limited length of the flights, after the dregs are full, the drill must be lifted out of the hole to unload the soil, and this operation is repeated (the cycle of “drilling → lifting → unloading → lowering the drill”).
Stronger Adaptability: It can handle slightly harder formations or gravel-containing soil layers by replacing the drill bit (e.g., conical teeth, flat-bottomed teeth).
2.Structural Features
Simple structure, low cost, suitable for shallow holes (<20m).
Can handle clay, cemented layers, or formations with a small amount of obstacles.
Low slag discharge efficiency; frequent drill lifting increases operation time.
3.Applicable Scenarios
Formations: Clay, cemented layers, or soil layers with a small amount of gravel; can handle slightly harder formations.
Project Types: Shallow hole operations such as small pile foundations, foundation pit support, and tree pit excavation.
Advantages: Simple structure, low cost, and strong adaptability.
4.Limitations
Low slag discharge efficiency and shallow drilling depth (generally <20m).
Frequent drill lifting increases operation time and is prone to causing hole wall disturbance.
III.Comparison Between Long Auger Drill and Short Auger Drill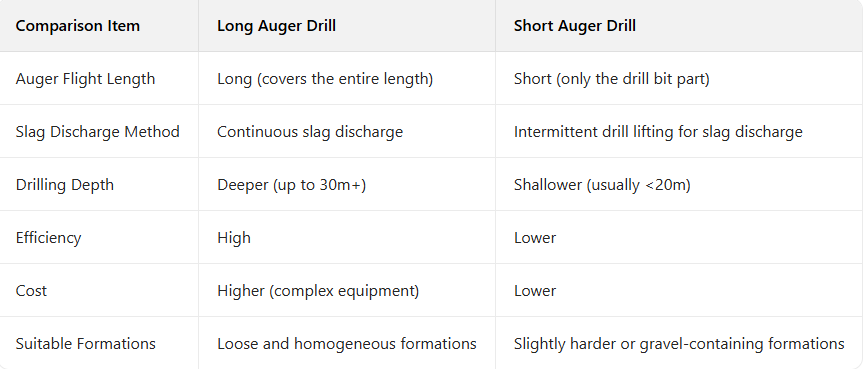
IV.How to Choose?
1.Prioritize Long Auger Drill: When fast hole formation, deep hole operation, and relatively homogeneous formations are required.
2.Prioritize Short Auger Drill: When the budget is limited, for shallow holes, or when the formation contains a small amount of obstacles.
Contact :Jessie Zhou
Mobile/Whatsapp:+0086-18109206861
Web: www.landrilltools.com
Post time: Sep-10-2025







 5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China
5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China  86-13609153141
86-13609153141 

