For the non-magnetic drill collars (NMDCs) used in directional drilling, post-use maintenance is critical to ensure stable performance, extend service life, and prevent magnetic interference or structural damage caused by improper handling, which could compromise downhole measurement accuracy. Below are detailed maintenance steps and precautions:
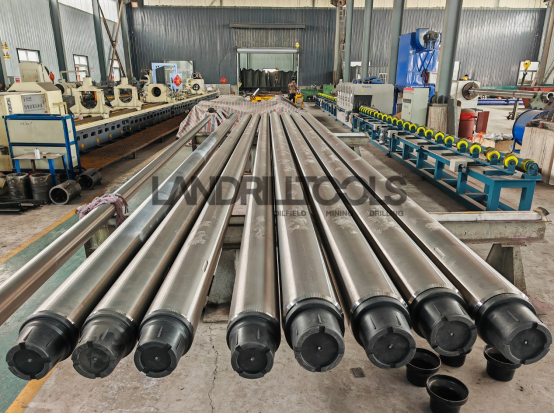

1. Post-Use Cleaning
- Removal of Mud and Deposits:
- Immediately rinse the internal and external surfaces of the drill collar with high-pressure water or specialized cleaning equipment to thoroughly remove drilling fluid, cuttings, grease, and other residues, preventing corrosion or scaling.
- Use neutral detergents (avoid acidic or strongly alkaline solvents) to prevent surface corrosion.
- Drying:
- After cleaning, use compressed air or dry cloths to ensure complete dryness, especially in threaded connection areas, to prevent rust from moisture retention.
2. Comprehensive Inspection
- Visual Inspection:
- Check for scratches, dents, cracks, or deformities on the collar surface, focusing on threaded connections and stress concentration zones (e.g., transition areas).
- Use magnifying tools or non-magnetic-compatible methods (e.g., dye penetrant testing) to detect micro-cracks.
- Thread Inspection:
- Inspect internal and external threads for wear, deformation, or corrosion. Use thread gauges to verify accuracy if necessary.
- Clean threads and apply non-metallic anti-rust grease.
- Magnetic Permeability Testing:
- Use a gaussmeter (Tesla meter) to measure magnetic field intensity across the collar, ensuring permeability meets standards (typically ≤1.05 μ).
- If localized magnetization is detected (due to stress or metal contamination), perform demagnetization (e.g., annealing or specialized degaussing).
3. Demagnetization (If Required)
- Annealing:
- Heat in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to the material’s annealing temperature (e.g., 600–800°C for Monel alloys) to eliminate residual stress and magnetism.
- Strictly follow manufacturer parameters to avoid overheating, which may cause intergranular corrosion or mechanical degradation.
- Localized Degaussing:
- Use electromagnetic degaussing equipment to target magnetized areas and restore non-magnetic properties.
4. Corrosion Prevention and Lubrication
- Anti-Corrosion Coating:
- Repair minor surface damage with touch-up paint or epoxy coatings to prevent corrosion spread.
- Thread Protection:
- Apply non-metallic lubricants (e.g., molybdenum disulfide-based grease) to threads to prevent wear and rust.
- Install thread protectors (e.g., plastic caps) during storage or transport.
5. Storage Management
- Environmental Requirements:
- Store in a dry, ventilated indoor environment with humidity below 60% and stable temperatures.
- Keep away from strong magnetic sources (e.g., motors, transformers).
- Positioning:
- Place horizontally on dedicated racks to avoid bending; never stack vertically or pile directly.
- Inspect storage conditions quarterly for rust or deformation.
6. Transport Protection
- Securing and Cushioning:
- Use dedicated fixtures with rubber pads or wooden blocks to prevent impacts during transit.
- Magnetic Shielding:
- Shield collars with anti-magnetic materials if transporting near magnetic sources.
7. Periodic Professional Testing
- Routine Testing:
- Conduct biannual/annual third-party lab tests, including:
- Permeability testing (per ASTM A342).
- Ultrasonic testing (UT) or radiographic testing (RT) for internal defects.
- Material composition analysis (e.g., spectrometry) to confirm non-magnetic integrity.
- Conduct biannual/annual third-party lab tests, including:
- Documentation:
- Maintain records of test results and maintenance actions for lifecycle tracking.
8. Operator Training
- Train personnel regularly on:
- Prohibiting steel tool impacts on NMDCs.
- Avoiding operation/storage near strong magnetic fields.
- Using torque wrenches to tighten threads per specifications.
Key Precautions
- Avoid Welding: NMDCs are generally non-weldable; repairs must be done by certified manufacturers.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure cleaning agents, lubricants, etc., are compatible with the collar material (e.g., Monel alloys are sensitive to ammonia; avoid ammonia-containing substances).
Systematic maintenance minimizes NMDC failure rates, ensuring directional drilling accuracy and operational safety. Replace or return severely damaged or magnetized collars to the manufacturer promptly.
PS:
LANDRILL can provides a full range of slick and spiral drill collars in NMDC with P530,P550,P650 and equivalent material. Contact us for the details.
Post time: May-15-2025







 5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China
5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China  86-13609153141
86-13609153141 

