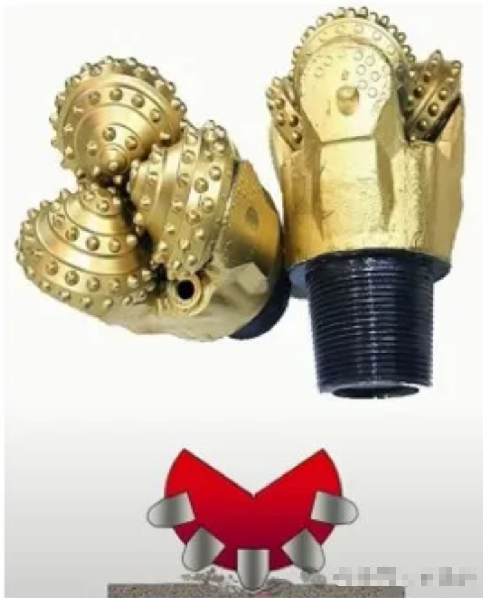
1. Tricone Drill Bits:
Rolling cutter bits (or rotary cone bits) have their cutting elements arranged on cones that rotate around their axes as the bit body spins. The number of cones on a bit can be 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. However, the most common rotary cone bits are tri-cone bits. Approximately 95% of oil and gas wells worldwide are drilled using rolling cutter bits, especially tri-cone bits. In soft formations, the teeth are longer and spaced further apart. For harder rocks, the tooth size and spacing are reduced.
- Single-Cone Bits: This type of bit rotates around its axis and is primarily used in directional drilling. These bits are applied in rotary drilling systems for fractured formations, abrasive formations, medium-hard formations, and angled surfaces. Single-cone bits minimize the likelihood of well deviation.
- Two-Cone Bits: Mainly used in soft formations and directional drilling.
- Tri-Cone Bits: Tri-cone bits are the most common type of bit, used in the majority of drilling operations worldwide.
Tricone drill bits can be divided into two categories:
i. Milled Tooth Tricone Bits (MT Bits):
Early models of MT bits had two cones, where the teeth and gullets on the cones did not contact during rotation. The contact between teeth on adjacent cones provides self-cleaning, increases penetration rate, and facilitates the drilling process. Milled tooth bits are used in soft to medium-hard formations.
ii. Tungsten Carbide Insert (TCI) Drill Bits:
Tungsten Carbide Insert (TCI) bits, also referred to as button bits (e.g., the MT type), feature rotating cones. Unlike MT bits, these bits are fitted with tungsten carbide buttons on the cones at extremely high installation temperatures. They are used for operations in hard and corrosive formations in shallow subsurface environments. At greater depths, tricone bits exhibit poor performance and are time-consuming to replace.
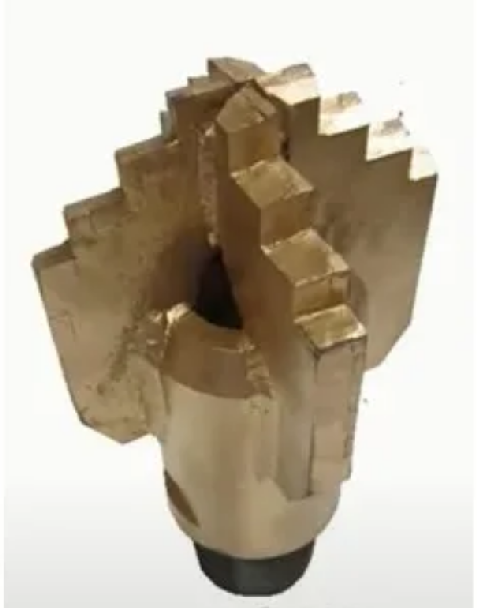
2. Fixed Cutter Drill Bits
Fixed cutter bits are of monolithic construction with no moving parts. In fact, this type of bit does not have independently rotating cones; instead, it features a stationary bit body and a fixed head that rotates in conjunction with the drill pipe and drill string. The main body of such bits is made of steel or tungsten carbide. Steel-body bits have high resistance to impact and forces applied to the cutters, but steel has low resistance to erosion caused by drilling fluids. Conversely, tungsten carbide-body bits have high resistance to erosion but are less resistant to impact.
i. Steel Cutter Bits
These bits are divided into two categories: steel cutter & fishtail bits, and drag bits. Drag bits are used for drilling in soft formations in the oil and gas industry. Drag bits were the first type of bit used in rotary drilling, but they were gradually replaced by cone bits due to low efficiency. These bits are equipped with steel cutters and are primarily used in soft formation drilling. Their usage frequency has decreased due to poor efficiency in hard formations; when high loads are applied to the bit, the steel cutters will embed into the formation, and increasing drill pipe torque can cause the drill pipe to break and fall into the well. This type of bit is difficult to control the wellbore path and often deviates from the main trajectory.
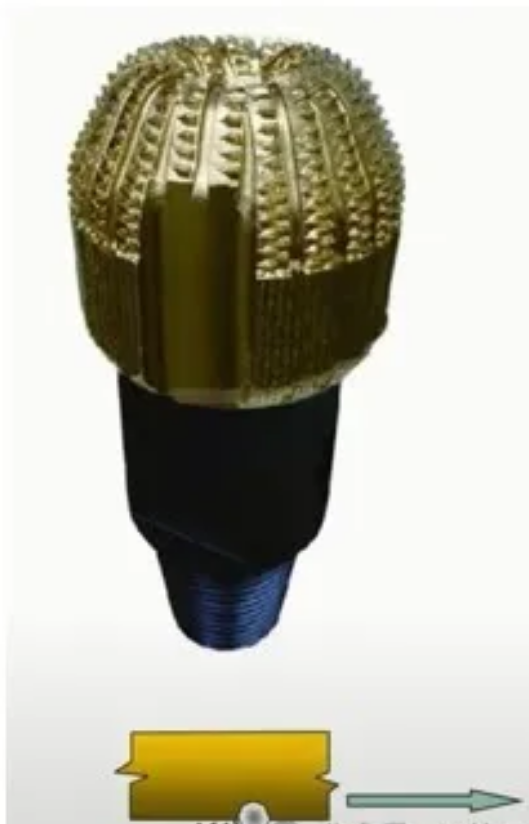
ii. Diamond Drill Bits
In this type of bit, diamond particles are embedded in the bit body. Diamond, the hardest known material, is composed of pure carbon. Due to its hardness, these bits are most suitable for drilling in abrasive hard formations. Compared to rolling cutter bits and steel cutter bits, diamond bits are less sensitive to drilling mud. Diluted drilling mud typically improves bit efficiency and is more economical.
Diamond bits offer numerous advantages, including increased drilling speed across various formations and rock layers, reduced tripping time and bit wear, no need for spare parts, and suitability for high-pressure wells and other special conditions.
Classification of Diamond Drill Bits
- Natural Diamond Drill Bits
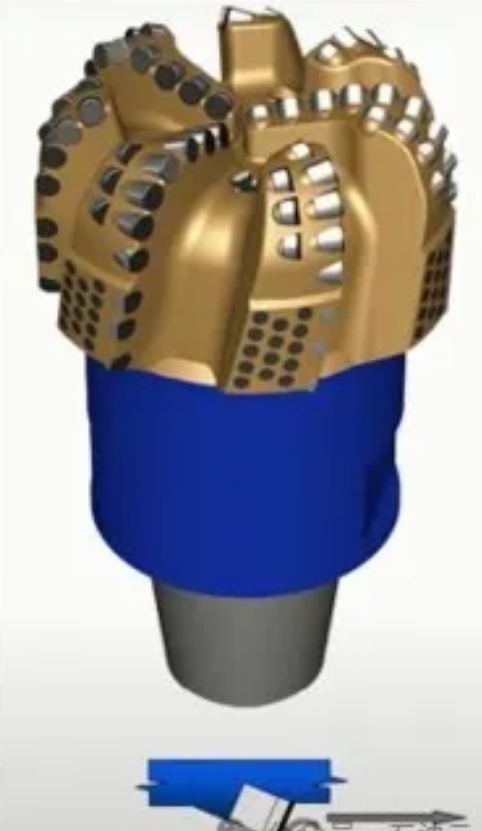
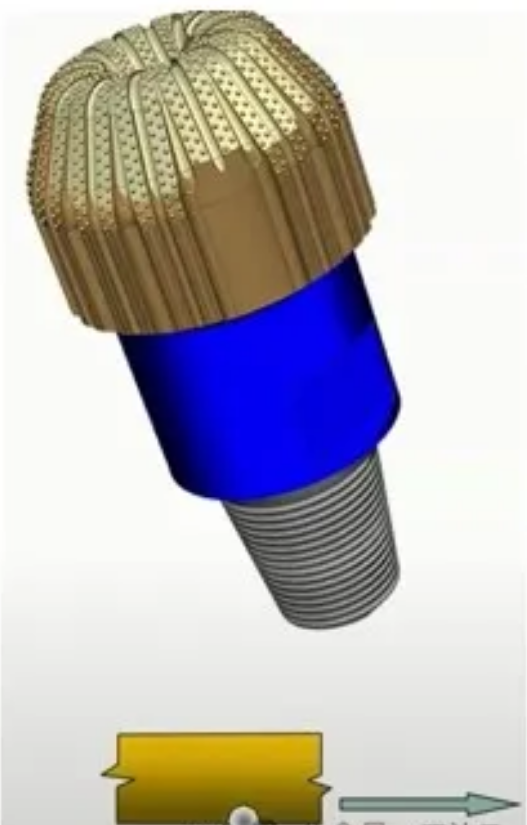
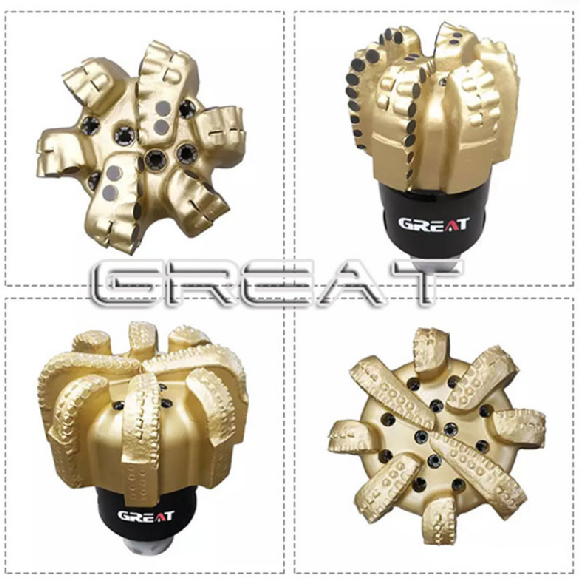
- Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Bits (PDC)
- Thermally Stable Polycrystalline Bits (TSP)
Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Bits (PDC):
PDC bits feature a tungsten carbide body with cutters mounted on the surface. These bits can be designed with or without nozzles. The size of diamond particles in PDC affects their impact resistance and wear resistance. Synthetic diamond, produced using cobalt as a catalyst, makes PDC less heat-resistant than natural diamond. When heated, cobalt expands and can cause diamond cracking.
• Thermally Stable Polycrystalline Bits (TSP):
TSP bits were developed to address the heat resistance limitations of PDC bits. During manufacturing, cobalt is removed via acid leaching, or silicon carbide is used to enhance heat resistance. As a result, TSP bits outperform PDC bits in extremely hard formations.
• Natural Diamond Drill Bits
Oil Drill Bits
Purpose of Drilling: Drilling is a critical process and tool for the exploration and development of oil and gas resources. In petroleum geological work, the primary objective of drilling is to obtain subsurface material data, which involves collecting physical samples such as cores, mineral cores, cuttings, fluids, and gases from the wellbore.
Application of Drill Bits in Petroleum Industry
As a geophysical logging channel, it enables the acquisition of various geophysical data from subsurface rock and mineral formations.As an artificial channel, it allows observation of subsurface geological conditions and underground fluid dynamics.Wellbores are used to extract subsurface petroleum, natural gas, groundwater, and geothermal resources.
Drilling technology is employed for the exploration and development of oil and natural gas, and mainly includes:
- Wellbore design
- Selection of drill bits and drilling fluids
- Assembly of drilling tools
- Coordination of drilling parameters
- Well deviation control
- Drilling fluid treatment
- Coring
- Accident prevention and handling
Petroleum drilling technology is characterized by deep well depth, high pressure, high temperature, and numerous influencing factors.
Types of Petroleum Drill Bits
Based on geological and geographical conditions and engineering requirements for oil and gas exploration and development, wells can be divided into two categories: vertical wells and directional wells. Directional wells can be further classified into conventional directional wells, horizontal wells, and clustered wells.
Drill bit types include PDC bits and Tricone bits.PDC bits are also widely used in standard petroleum drilling operations, offering advantages such as high efficiency and stable performance.
First, based on the difference in materials, PDC bits can be divided into steel-body PDC bits and matrix-body PDC bits.
GREAT is equipped with advanced drilling parameter optimization software. Using electronic computers as a tool and optimization methods, it establishes mathematical models and develops programs based on the minimum cost principle, incorporating various controllable factors affecting drilling speed (such as bit type, bit pressure, rotational speed, mud performance, and hydraulic factors). These models are used to optimize and coordinate operations, enabling drilling projects to achieve high quality, high speed, and low cost.
Core Extraction Technology Using Oil Drill Bits
Core extraction technology involves drilling rock samples (cores) from target intervals in boreholes according to design requirements, to obtain first-hand data for the exploration and development of oil and gas reservoirs.
Common coring tools mainly consist of diamond coring devices, core barrels, core grabs, and joints. During coring, the bit continuously cuts the bottomhole rock in a circular pattern, allowing the drilled cylindrical core to enter the core barrel continuously.
To meet special requirements for extremely loose and fractured formations, specialized coring methods and tools are available, including sealed coring, pressure-controlled coring, and rubber sleeve coring tools.
Contact :Jessie Zhou
Mobile/Whatsapp:+0086-18109206861
Email: energy@landrilltools.com
Post time: Jan-23-2026















 5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China
5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China  86-13609153141
86-13609153141 

