API Drill Pipe Thread Types: The Ultimate Guide to Drilling Connections
In the drilling industry, every component plays a vital role in the success of operations. Among the most critical are API drill pipe thread types—these unsung components ensure the smooth transmission of downhole power and fluid circulation. Understanding these connections is not just technical knowledge; it is a way to enhance drilling efficiency, safety, and profitability.
This ultimate guide will take an in-depth look at various API drill pipe thread types, from conventional connections to designated connections. We will explore their unique characteristics, applicable scenarios, and their key impacts on drilling operations, helping you make informed decisions to achieve superior performance.
What is API Drill Pipe Thread?
API drill pipe threads refer to the standardized threaded connections on drill pipes that comply with the standards of the American Petroleum Institute (API), especially API Specification 5DP.
These API connections ensure the compatibility, robustness, and reliable sealing performance of the drill string in demanding oil and gas drilling operations.
What is a drill pipe thread?
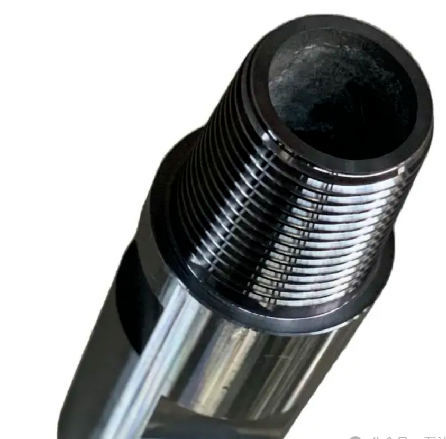
Drill pipe threads refer to special mechanical connection structures machined at the ends of each drill pipe segment. Through this connection, each segment of drill pipe can be joined together to form a continuous drill string. These threads are carefully designed with specific profiles, tapers and dimensions to ensure a secure, high-strength connection that can transmit rotational torque, downward pressure and typical drilling fluid pressure.
The male end is called the “pin”, which has external threads on its surface; the female end, known as the “box”, has corresponding internal threads. The design of these threads is critical to maintaining the integrity of the drill pipe under the extreme pressures encountered in drilling operations, helping to avoid costly failures and ensure efficient well construction.
API Drill Pipe Thread Types
The American Petroleum Institute (API) has established multiple standardized thread types for drill pipes, which is crucial for ensuring compatibility, strength, and reliable connections within the drill pipe system. These thread types are carefully designed to handle the extreme pressures and operational requirements encountered during oil and gas drilling.
Understanding each type is key to optimizing drilling performance and avoiding major failures.
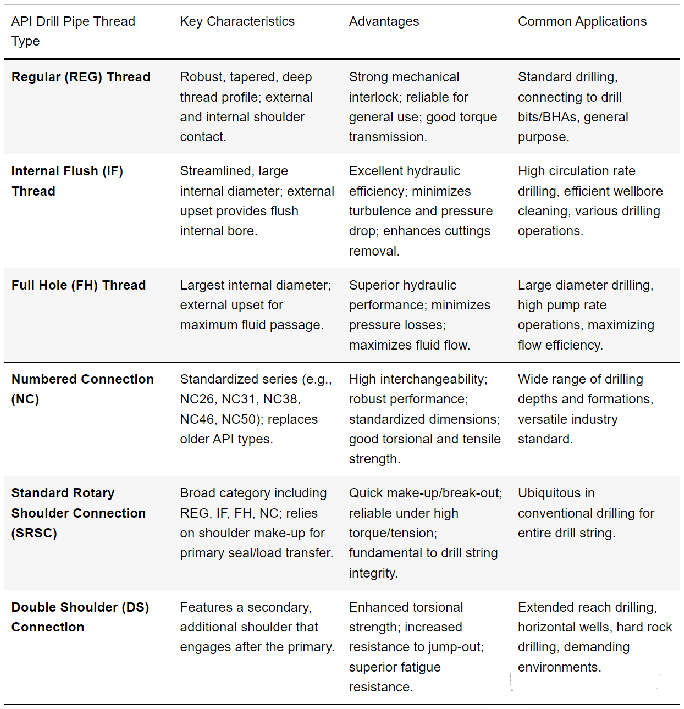
Below are the main API drill pipe thread types:Standard (Conventional) Threads
The API Regular (REG) thread is a classic and robust connection method, designed specifically for general-purpose drilling applications. It features a deep thread profile and tapered design, which enables a secure mechanical engagement between the pin end and box end of the drill pipe. This design ensures that torque and axial loads can be efficiently transmitted along the drill string.
Although widely used (especially for connecting drill bits and bottom-hole assembly components), the inner diameter of REG threads is smaller than that of some other API connection types. This leads to slightly higher pressure loss when circulating drilling fluid, but its reliability and ease of use make it a common choice in many standard drilling scenarios.
Internal Flush (IF) Threads
The design of API Internal Flush (IF) threads focuses on optimizing hydraulic efficiency. It is engineered to create a smooth, continuous internal passage through the connection, thereby minimizing turbulence and pressure loss when drilling fluid passes through the drill pipe. This “flush” internal diameter is achieved by thickened pipe ends (flared), which accommodate the threads without restricting the fluid passage.
This improved fluid flow is particularly beneficial in operations requiring high circulation rates, or when drilling through rock formations that generate large amounts of cuttings, as it can clean the wellbore walls and cool the drill bit more effectively. Despite its excellent hydraulic performance, the larger outer diameter of the tool joint may sometimes lead to increased wear in highly abrasive rock formations.
API Full Hole (FH) threads are another connection type designed to maximize the internal fluid passage. Similar to IF threads, their internal diameter is typically larger. This design minimizes the flow resistance of drilling fluid, which is critical for maintaining optimal hydraulic performance—especially in large-diameter drilling or applications requiring high pump rates.
FH connections are particularly advantageous in scenarios where maximizing fluid return rates and minimizing pressure loss are priorities. This connection is usually applied to larger-diameter drill pipes and is selected when the highest possible fluid delivery efficiency through the drill string is prioritized, thereby helping to increase drilling speed and clean the wellbore more effectively.
Numbered Connections (NC)
The launch of the API Numbered Connection (NC) series aims to standardize and replace many older API thread designs, including some IF and FH connections. The “NC” designation is followed by a number, which represents the approximate pitch diameter of the thread (in inches and tenths of an inch), thus forming a clear and consistent naming convention.
NC connectors have extremely high versatility and a wide range of industry applications, thanks to their standardized dimensions and excellent performance. Their design can withstand high-strength torque and tensile stress, making them suitable for various drilling depths and complex geological conditions. Interchangeability simplifies inventory management and ensures compatibility between different drilling equipment.
Standard Rotating Shoulder Connection (SRSC)
The Standard Rotating Shoulder Connection (SRSC) is a broad category that includes various tapered rotating shoulder connections widely used in the drilling industry, such as API threads (e.g., REG, IF, FH, and NC). These connections rely on a precision-machined “shoulder” to “make up” (achieve tight contact), thereby providing primary sealing and transmitting compressive loads. The threads mainly serve to pull the shoulders together and transfer rotational loads.
The SRSC design is critical to drill string integrity, enabling quick and safe assembly and disassembly while ensuring excellent performance. It has exceptional reliability in high-torque and high-tension environments, so it is extremely common in conventional drilling applications, forming the main body of most drill strings from surface to bottom-hole assembly components.
Double Shoulder (DS) Connection Method
The Double Shoulder (DS) Connection is an advanced proprietary or high-end thread design that offers significantly improved performance compared to standard API connections, as it adds a second shoulder to the base of the standard thread. This second shoulder engages after the first one, providing additional contact points and load-bearing capacity. This innovative design greatly enhances the connection’s torsional strength and pull-out resistance.
The added shoulder design in DS connections allows them to withstand higher torque values and offers excellent fatigue resistance, making them highly suitable for use in challenging drilling environments such as long-reach drilling, horizontal drilling, or operations in hard, abrasive formations. Their enhanced robustness helps improve drilling efficiency and reduce non-productive time.
Below is a table listing the various types of API drill pipe thread types:
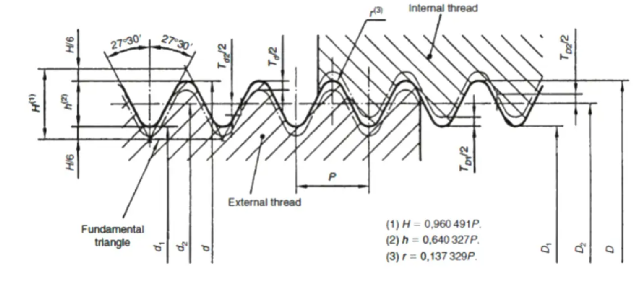
API Drill Pipe Thread Dimensions
Contact :Jessie Zhou
Mobile/Whatsapp:+0086-18109206861
Email: energy@landrilltools.com
Post time: Jan-12-2026















 5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China
5-1203 Dahua Digital Industrial Park Tiangu 6th Road,Hi-tech development Zone Xi'an, China  86-13609153141
86-13609153141 

